| ETHYLENEGLYCOL MONOPROPYL ETHER | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 2807-30-9 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 220-548-6 | |
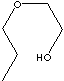
| FORMULA | C3H7OCH2CH2OH | |
| MOL WT. | 104.15 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2909.42 | |
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 3089 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Propyl cellosolve; 2-Propoxyethanol; 3-Oxa-1-hexanol; | |
| ethylene glycol monopropyl ether; propoxyethanol; Propyl glycol; | ||
|
SMILES |
||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Clear liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | -90 C | |
| BOILING POINT |
149 -150 C |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.913 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Freely soluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | 3.6 | |
| AUTOIGNITION |
230 C |
|
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2 Flammability: 2 Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT |
52 C |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable at ordinary conditions |
|
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
Glycol: any of a class of organic chemicals characterized by having separate two
hydroxyl (-OH) groups, contribute to high water solubility, hygroscopicity and
reactivity with many organic compounds, on usually linear and aliphatic carbon
chain. The general formula is CnH2n(OH)2 or (CH2)n(OH)2. The wider meaning names
include diols, dihydric alcohols, and dihydroxy alcohols. Polyethylene glycols
and polypropylene glycols are sometimes called polyglycols which are derived by
polymerization of ethylene oxide and propylene oxide respectively. Polyethylene
glycols are water-soluble at all molecular weights, but polypropylene glycols
become increasingly less water-soluble at high molecular weights. Ethylene
glycol, HOCH2CH2OH, is the simplest member of the glycol family. Mono-, di- and
triethylene glycols are the first three members of a homologous series of
dihydroxy alcohols. They are colourless, essentially odourless stable liquids
with low viscosities and high boiling points. Ethylene glycol is a
colourless, odourless, involatile and hygroscopic liquid with a sweet taste. It
is somewhat viscous liquid; miscible with water; boiling point 198 C, melting
point 13 C; soluble in ethanol, acetone, acetic acid, glycerine, pyridine,
aldehydes; slightly soluble in ether; insoluble in oil, fat, hydrocarbones. It
is prepared commercially by oxidation of ethylene at high temperature in the
presence of silver oxide catalyst, followed by hydration of ethylene oxide to
yield mono-, with di-, tri-, and tetraethylene glycols as co-products. The
yields of ethylene glycol are depend on pH conditions. The acid-catalyzed
condition in the presence of excess water provides the highest yield of
monoethylene glycol. Because of its low freezing point, involatility and low
corrosive activity, it is widely used in mixtures of automobile antifreeze and
engine-cooling liquids. Ethylene glycol has become increasingly important in the
plastics industry for the manufacture of polyester fibers and resins, including
polyethylene terephthalate, which is used to make plastic bottles for soft
drinks (PET bottles). MEG is the raw material in the production of polyester fiber, PET resins,
alkyd, and unsaturated polyester. Diethylene glycol, CH2OHCH2OCH2CH2OH, is similar in
properties to MEG, but with a higher boiling point, viscosity, and specific
gravity. Diethylene glycol is used in the manufacture of unsaturated polyester
resins, polyurethanes and plasticizers. It is a water-soluble liquid; boiling
point 245 C; soluble in many organic solvents. It is used as a humectant in the
tobacco industry and in the treatment of corks, glue, paper and cellophane.
Diethylene glycol (DEG) is derived as a co-product with ethylene glycol and
triethylene glycol. The industry generally operates to maximize MEG production.
Ethylene glycol is by far the largest volume of the glycol products in a variety
of applications. Availability of DEG will depend on demand for derivatives of
the primary product, ethylene glycol, rather than on DEG market requirements.
Triethylene glycol, HO(C2H4O)3H, is a colourless, odourless, non-volatile, and
hygroscopic liquid. It is characterised by two hydroxyl groups along with two
ether linkages, which contribute to its high water solubility, hygroscopicity,
solvent properties and reactivity with many organic compounds. DEG is used in
the synthesis of morpholine and 1,4-dioxane. TEG is displacing
diethylene glycol in many of these applications on account of its lower
toxicity. TEG finds use as a vinyl plasticizer, as an intermediate in the
manufacture of polyester resins and polyols, and as a solvent in many
miscellaneous applications. Triethylene glycol (TEG) is derived as a coproduct
in the manufacture of ethylene glycol from ethylene oxide, and from "on-purpose"
TEG production using diethylene glycol. Some capacities are based on total
capacity for ethylene glycols. The main uses for TEG depend upon its hygroscopic
properties. Air conditioning systems use TEG as dehumidifiers and, when
volatilized, as an air disinfectant for bacteria and virus control. Glycols,
having high boiling point and affinity for water, are employed as liquid
desiccant for the dehydration of natural gas. The dehydration means the removal
of water vapor in refinery tower so that dry hydrocarbon gases can exit from the
top of the tower. There are wide range of glycol ethers which have bifunctional
nature of ether and alcohol. cellosolves are monoether derivatives of ethylene
glycol. They are excellent solvents, having solvent properties of both ethers
and alcohols. Glycol family products are versatile compounds used in the fields
include;
Glycol ethers, with the combination of ether, alcohol and hydrocarbon chain in one molecule, provide versatile solvency characteristics with both polar and non-polar properties. The chemical structure of long hydrocarbon chain resist to solubility in water, while ether or alcohol groups introduce the promoted hydrophilic solubility performance. This surfactant-like structure provides the compatibility between water and a number of organic solvents, and the ability to couple unlike phases. Glycol ethers are characterized by their wide range of hydrophilic/hydrophobic balances. glycol ethers are used as diluents and levelling agents in the manufacture of paints and baking finishes. Glycol ether series are used in the manufacture of nitrocellulose and combination lacquers. They are used as an additive in brake fluid. They are formulated for dying textiles and leathers and for insecticides and herbicides. They provides performance in cleaners products with oil-water dispersions. They are used in printing industries as they have a slow evaporation rate. They are used as a fixative for perfumes, germicides, bactericides, insect repellents and antiseptic. They are used as an additive for jet fuel to prevent ice buildup. Glymes, dimethyl ethers, have two terminal methyl groups which offer stability and high solvency. They are useful as solubilizers and phase transfer catalysts. Glymes offer the property required as an inert reaction medium chemical reaction due to their low chemical reactivity. They are suitable particularly for organometallic and polymerization reactions. Glycol ethers which contain hydroxyl group are also useful chemical intermediate. The hydroxyl group will undergo reaction with aldehydes (or ketones) to produce hemiacetals (or acetals), with epoxides to produce polyether alcohols, with halogenating agents to produce alkoxy alkyl halides, with carboxylic acid compounds or inorganic acids to produce a number of esters. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid | |
|
SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
0.912 - 0.914 | |
| DISTILLATION IBP |
146 C |
|
| DISTILLATION DP |
151 C |
|
|
MOISTURE |
0.1% max |
|
|
ACIDITY |
0.01% max |
|
|
COLOR, APHA |
20 max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 190kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 3 (Packing Group: III) | |
| UN NO. | 1171 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN XI F, Risk Phrases: 10-21-36, Safety Phrases: 24/25-36/37 | ||